Pulmonary nodules malignancy prediction in CT images
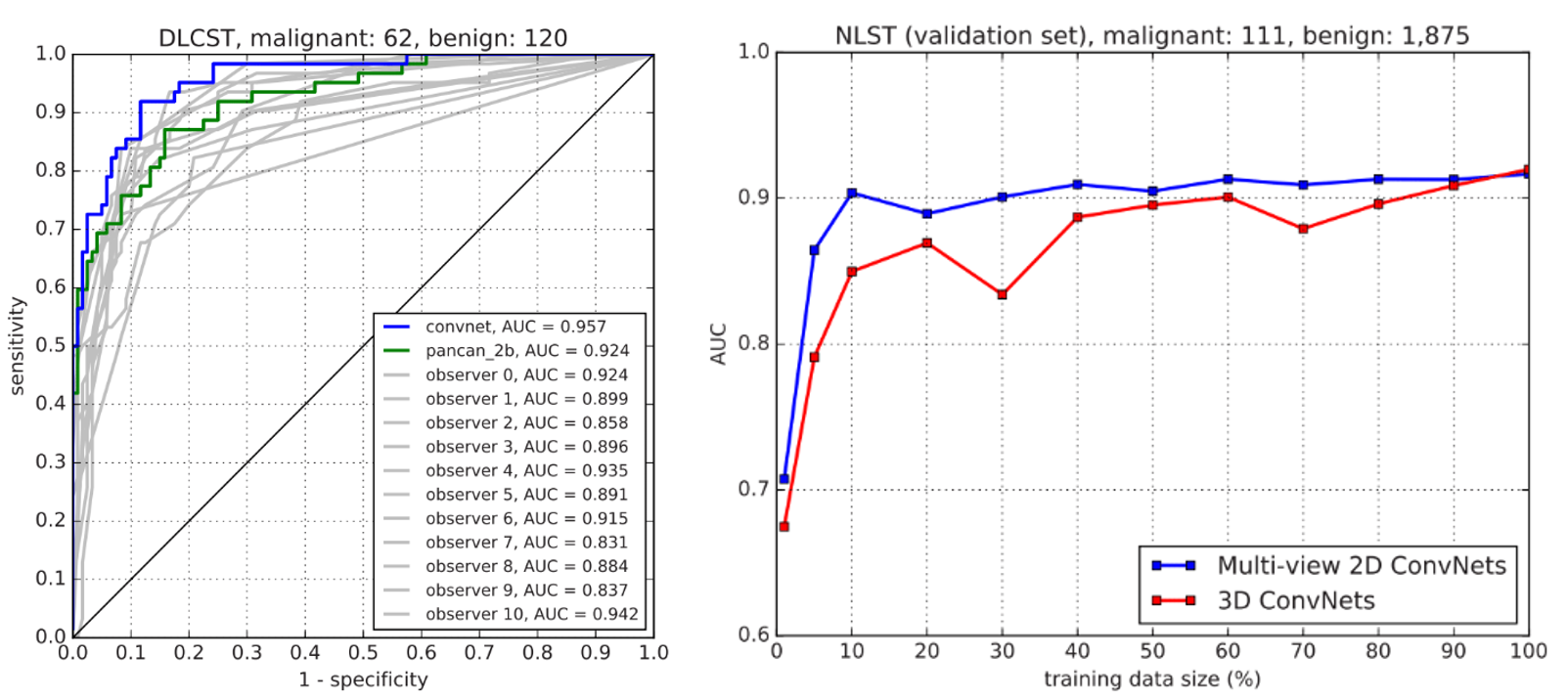
Early stage lung cancer manifests itself as focal abnormalities in the lung called pulmonary nodules. The vast majority of nodules found in screening participants are eventually benign. Follow-up of benign nodules can lead to unnecessary imaging or invasive follow-up procedures. A data-driven model that can accurately predict nodule malignancy from CT data may improve management decisions and increase the effectiveness of lung cancer screening programs.
Within this project, we develop and validate a deep learning algorithm based on convolutional neural networks for pulmonary nodule malignancy prediction and to compare its performance against expert readers and an established multivariate prediction model. The results were summarized in my PhD Thesis. This study was further expanded by Kiran Venkadesh and was published in Radiology.
Publications
- K. V. Venkadesh, A. A. A. Setio, A. Schreuder, E. T. Scholten, K. Chung, M. M. W. Wille, Z. Saghir,B. van Ginneken, M. Prokop, and C. Jacobs, “Deep learning for malignancy risk estimation of pulmonary nodules detected at low-dose screening CT,” Radiology, vol. 300, no. 2, pp. 438–447, 2021 link
- A.A.A. Setio, ”Computer-aided diagnosis in thoracic CT scans for lung cancer screening”, 2018. link